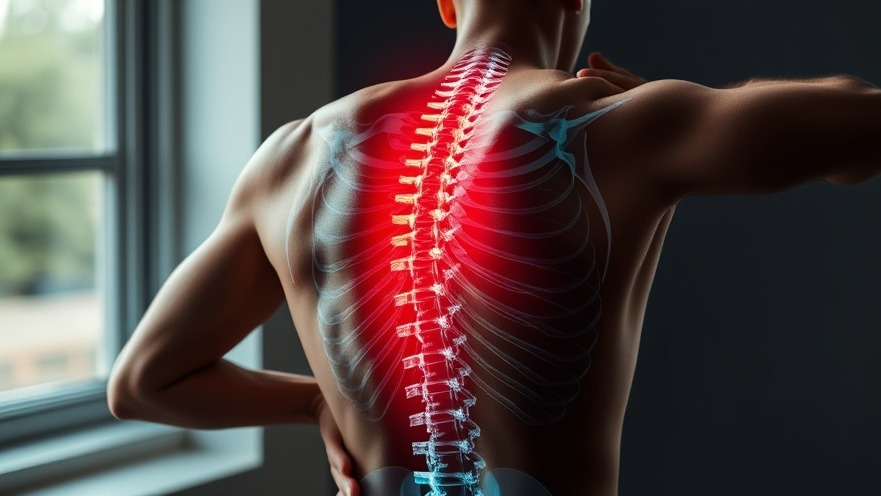
Understanding Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH)
Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis, commonly referred to as DISH or Forestier disease, is a form of arthritis that primarily impacts the tendons and ligaments surrounding the spine. This condition can cause the soft tissues to calcify, forming bone spurs that can hinder mobility and lead to discomfort. While many individuals with DISH may remain symptomless, those who do experience symptoms may face significant challenges in daily life, particularly with back pain and stiffness.
Identifying Symptoms
For the majority of those affected, DISH may go unnoticed until an imaging test uncovers it. However, when symptoms do arise, they can include:
Morning stiffness that enhances during the day.
Pain localized in the neck or upper back.
Restricted range of motion of the back.
It can also lead to complications such as hoarseness, difficulty swallowing, or tingling sensations in the legs due to nerve compression.
As concierge medical practitioners, understanding these manifestations is crucial as they can aid in earlier diagnoses and tailored patient care.
The Health Impact of DISH
While back pain is a common symptom, DISH can escalate into serious health issues. Bone spurs can compress vital structures such as the esophagus, potentially leading to swallowing difficulties and complicating the patient's nutritional health. Furthermore, the risk of spinal fractures becomes a distinct concern as the condition progresses.
Understanding the Roots of DISH
The exact cause of DISH remains elusive, with a combination of genetic, environmental, and metabolic factors thought to contribute to the disease. For example, it is more prevalent in men over the age of 50 and those with diabetes or obesity. A peculiar link has also been observed with certain medications like isotretinoin, although the directional causality is still under investigation. This knowledge can significantly influence how concierge medical practices approach patient education regarding lifestyle factors.
Diagnosing and Treating DISH
DISH cannot be reversed, but effective management strategies exist. Diagnosis typically involves physical examinations and imaging tests such as x-rays and MRIs, which also differentiate DISH from other arthritis forms. Treatment options focus on alleviating symptoms:
Physical therapy and regular exercise can help improve mobility and reduce pain, particularly beneficial exercises like swimming.
Heat therapy may ease morning stiffness.
Maintaining a healthy weight and managing blood sugar levels are key to reducing symptom severity.
Utilizing orthotics can help alleviate discomfort associated with bone spurs.
For pain relief, over-the-counter medications can provide necessary support.
These treatment strategies not only help manage symptoms but align with the holistic approach of many concierge practices to emphasize overall wellness.
Empowering Patients Through Knowledge
As professionals in concierge medical practice, it is vital to bridge the gap between complex health phenomena like DISH and patient understanding. By providing clear, empathetic communication about the condition, its implications, and avenues for management, practice owners can foster trust and encourage patients to be proactive about their health. Additionally, taking the time to address how lifestyle choices impact DISH could empower patients and enhance their engagement with treatment plans.
Understanding DISH and its implications can vastly improve patient care and create an environment of support that emphasizes empathy, wellness, and long-term health strategies. By prioritizing patient relationships and open communication, concierge medical practices can establish themselves as leaders in comprehensive care.
Take Action: Educate Yourself and Your Patients—By staying informed about conditions like DISH and adopting a holistic approach to health, you can better serve your patients and enhance their overall satisfaction with your concierge services.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 



Write A Comment