Revolutionizing Wound Healing: The Role of Fat-Derived Stem Cells
Stem cells extracted from adipose tissue may hold the key to advancing wound healing and improving scar formation, according to new research from Dr. Lisa Ramaut at the Brussels University Hospital. Published in the Aesthetic Surgery Journal Open Forum, this study emphasizes the potential application of adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs) in reconstructive surgery, paving the way for not only better clinical outcomes but also improved patient satisfaction.
Understanding Adipose-Derived Stem Cells
Adipose tissue has emerged as a promising source of mesenchymal stem cells, which are known for their ability to differentiate into various cell types and secrete growth factors vital for tissue regeneration. Traditional sources of stem cells include bone marrow and umbilical cord blood, which are often less accessible. In 2001, it was revealed that adipose tissue contains these beneficial stem cells, making it a more readily available option for therapeutic applications.
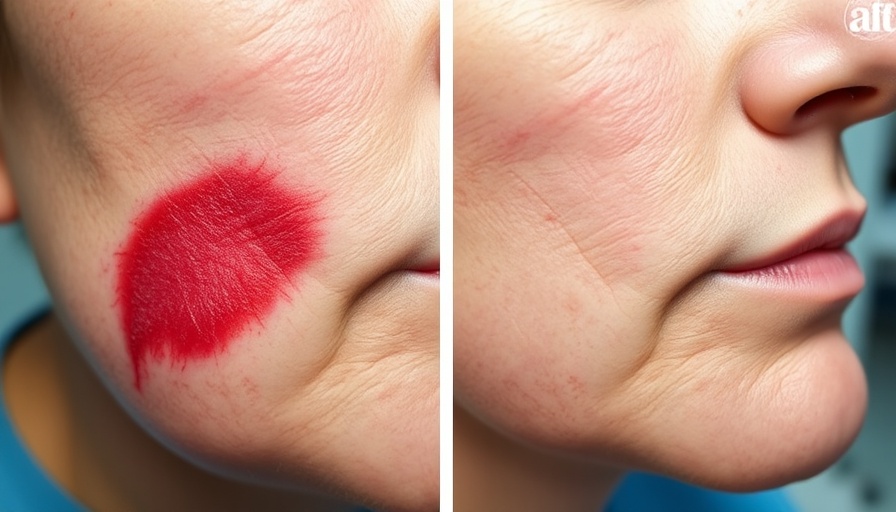
How Nanofat Enhances Scar Healing
In her study, Dr. Ramaut specifically investigated a treatment known as nanofat—small particle formulations derived from adipose tissue. These were applied to surgical wounds, resulting in a significant decrease in inflammation and redness in treated scars compared to control groups. Early results showcase that nanofat aids the initial phase of scar maturation, potentially reducing the likelihood of problematic scar formation long-term.
The Broader Implications for Plastic Surgery
This research is significant not just for surgical practices, but also in cosmetic procedures where scar formation can lead to adverse aesthetic outcomes. As outlined in the reference studies, ADSCs are capable of secreting angiogenic factors that expedite wound healing—important for patients suffering from chronic and challenging wounds, including venous ulcers and surgical complications. Given that more than 600,000 patients struggle with nonhealing wounds annually in the U.S., the demand for innovative treatment options is ever-growing.
Future Prospects and Research Directions
While the results from Dr. Ramaut's study are promising, they also highlight the need for larger clinical trials to substantiate the efficacy and safety of nanofat therapies. The unique therapeutic properties of ADSCs, including their ability to promote local blood vessel formation and modulate immune responses, suggest exciting future applications across both medical and cosmetic fields. As we move forward, comprehensive research will be pivotal in redefining standards of care in wound management.
Challenges and Perspectives in Utilizing ADSCs
Despite the promising advantages offered by ADSCs, clinicians must navigate several challenges including the standardization of extraction and application protocols. Furthermore, understanding the interactions between ADSCs and different tissue environments remains an essential area of research. Integrating technology in these avenues will also be crucial; for instance, using telemedicine to provide remote consultations and continuous patient monitoring post-treatment.
Taking Action: How Practitioners Can Prepare
For concierge health practitioners eager to enhance their treatment offerings, staying informed about advancements in ADSC research is imperative. Exploring partnerships with research institutions or attending relevant workshops can prepare practitioners for incorporating these innovations into their services. Educating patients about the potential benefits and risks associated with adipose-derived stem cell therapies will also foster stronger practitioner-patient relationships.
As medical professionals, knowing the cutting-edge practices in stem cell therapy illustrates a commitment to improving patient outcomes. The utilization of adipose-derived stem cells is not just a trend, but potentially a cornerstone of modern regenerative medicine.
To embrace the future of wound care and potentially transform patient experiences, consider researching more about adipose-derived stem cell treatments and discuss them with colleagues in the field. The positive effects we are beginning to observe could shape the landscape of wound healing in unimaginable ways!
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 




Write A Comment