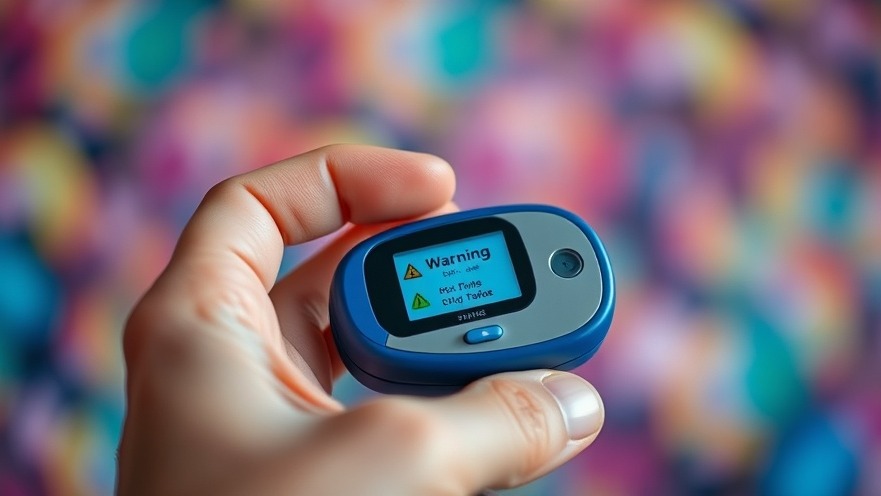
Empowering Safety: The Role of Continuous Glucose Monitoring for Diabetic Drivers
Driving can be a difficult task for individuals living with diabetes, particularly when managing the risk of hypoglycemia. A recent study conducted by Nagoya University has illuminated a promising approach to enhancing the safety of diabetic drivers through the use of continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) devices. This article examines the study's findings and implications, emphasizing the importance of real-time blood glucose monitoring for sustained driving confidence and safety.
Understanding the Risks of Hypoglycemia While Driving
Hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar, poses a significant risk to drivers with diabetes, leading to impaired judgment and potentially dangerous situations on the road. With over 422 million adults diagnosed with diabetes globally, the potential for hypoglycemic episodes while driving raises concerns about public safety. The physiological impairments caused by hypoglycemia—such as reduced attention and decision-making capabilities—can persist even after blood glucose levels return to normal. This makes it imperative for drivers with diabetes to manage their glucose levels effectively.
How Continuous Glucose Monitoring Devices Work
CGM devices utilize sensors attached to the skin to continuously monitor blood sugar levels, alerting users through sounds and vibrations when their levels drop below a critical threshold. This constant feedback allows users to take proactive measures to stabilize their glucose levels before it potentially impacts their ability to drive. In the Nagoya University study, participants used CGMs to gauge the effectiveness of these devices in preventing hypoglycemia during driving.
Study Findings: Confidence and Safety on the Road
The results of the study revealed that when diabetic drivers utilized CGM devices with active low-glucose alerts, the incidence of hypoglycemia while driving significantly decreased. Participants experienced a remarkable boost in confidence, with 63% reporting an increase in their ability to drive safely. The interaction of timely alerts and continuous monitoring allowed these drivers to remain attentive and prepared, effectively mitigating the risks associated with low blood sugar. As Dr. Hiroshi Arima commented, "CGM with low-glucose alerts can potentially reduce the risk of hypoglycemia for insulin-treated drivers," reinforcing the value of this technology.
Broader Implications for Public Safety
These findings not only highlight the personal benefits for diabetic drivers but also emphasize a broader implication for public safety. Reducing hypoglycemic episodes in drivers can lead to lower accident rates on the roads, enhancing the safety of all road users. The integration of CGM technology serves as a proactive intervention that can significantly change driving dynamics for those with diabetes.
Future Directions: Evolving Technology and Research
As CGM technology continues to advance, researchers are hopeful that increased accuracy and responsiveness will lead to further benefits in driving safety. Future studies could expand on this work by exploring the integration of CGM readings with vehicle technologies for real-time driving adjustments and safety interventions. Through continuous innovation, the goal is to ensure that individuals with diabetes can navigate the roads with confidence.
Common Misconceptions Regarding Diabetic Drivers
One of the prevalent misconceptions is that diabetes automatically disqualifies individuals from safe driving. However, studies like the one from Nagoya University demonstrate that with the right tools and strategies, many diabetic individuals can drive safely. The key lies in effective management of their condition and the use of supportive technology such as CGM devices.
Tools and Techniques to Enhance Driving Safety
For healthcare practitioners, understanding the role of CGM devices could reposition how diabetes management is approached, especially for patients with driving responsibilities. By educating patients on the benefits of CGMs, healthcare professionals can encourage safer driving practices and provide vital support for those who may fear driving due to previous hypoglycemic episodes.
In conclusion, as the world increasingly embraces technology to assist in chronic disease management, CGM devices stand out as a crucial development for diabetic individuals behind the wheel. These devices not only improve personal safety and confidence but also have the potential to make roads safer for everyone. Advocacy for greater access and awareness of CGM technology can empower patients and enhance public safety, ensuring that diabetes does not obstruct independence and mobility.
For more insights into managing diabetes and advances in healthcare technology, consider exploring additional resources and discussions. Your patients deserve the best tools to maintain their well-being.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 





Write A Comment