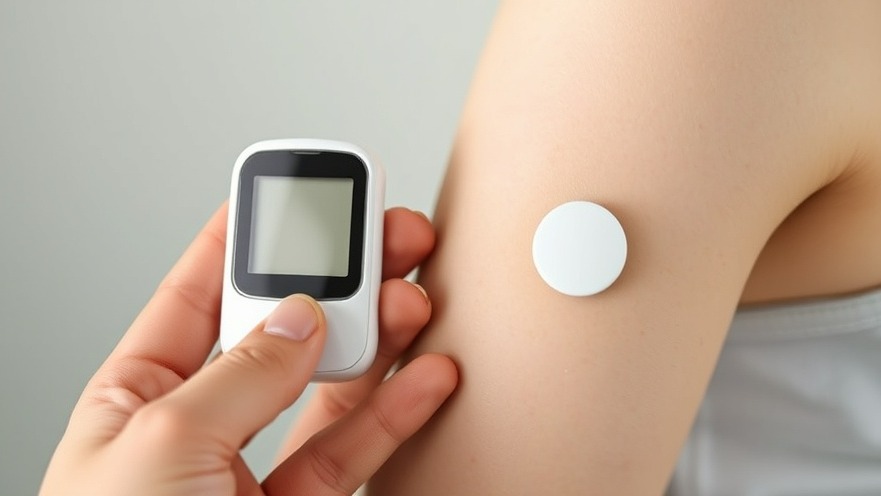
Harnessing Continuous Glucose Monitoring to Combat Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) remains a critical challenge in diabetes management, leading to significant healthcare costs and patient distress. Recent research highlights the pivotal role of continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) in transforming the management of DKA and preventing unnecessary ICU admissions.
Understanding Diabetic Ketoacidosis
DKA is a severe complication arising from insufficient insulin production, prompting the body to break down fat for fuel, which escalates acid levels in the bloodstream. Symptoms can develop rapidly, often including excessive thirst, weakness, nausea, and confusion. Hospitalizations for DKA account for more than 500,000 days annually in the U.S. alone, imposing an estimated healthcare burden of $2.4 billion.
The Promise of Continuous Glucose Monitors
A recent study by scientists at the University of Michigan evaluated the accuracy and efficacy of CGMs during DKA treatment. Traditionally, monitoring blood glucose levels required multiple painful fingerstick tests, which pose discomfort for patients and significant workload for healthcare providers. In contrast, CGMs offer a non-invasive monitoring solution by continuously measuring glucose levels through interstitial fluid, making it a preferable tool for DKA management.
Groundbreaking Research Outcomes
The Michigan study juxtaposed 334 simultaneous readings from CGMs and standard fingersticks on 20 DKA patients. Remarkably, results showed that CGMs were not only accurate but also outperformed fingersticks in detecting rapid declines in glucose levels. Dr. Nate Haas, a key investigator, emphasized the potential of CGMs to improve patient outcomes while concurrently alleviating the demand on crowded ICUs.
Historical Context and Technological Evolution
CGMs have been transformational for many diabetic patients, particularly children. According to earlier research, the introduction of CGMs in pediatric patients with type 1 diabetes not only improved overall glycemic control but significantly reduced DKA incidents. This trend suggests that expanding the use of CGMs into acute settings like DKA treatment could yield similar benefits, enhancing care quality and patient safety.
Cost-Effectiveness of CGMs in DKA Management
Beyond improving patient comfort and care quality, CGMs also present a financial advantage. The ability to reduce fingersticks can translate into fewer nursing hours dedicated to glucose monitoring, which in turn decreases overall hospital costs related to DKA care. In light of rising healthcare costs, adopting CGMs for DKA management appears to be a prudent investment.
Anticipating Future Trends in Diabetes Management
The advent of smart technology integration in diabetes management is likely to become standard practice. With continuous improvements in CGM technology and data analytics, we can anticipate more personalized diabetes management techniques that optimize treatment strategies and pave the way for better health outcomes.
Final Thoughts and Call to Action
For health practitioners navigating the complexities of DKA care, understanding and utilizing CGMs can significantly influence patient management and satisfaction. As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, embracing these technologies and advocating for their implementation could change lives. Consider integrating continuous glucose monitoring into your practice and stay proactive in enhancing patient outcomes in DKA management.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 





Write A Comment