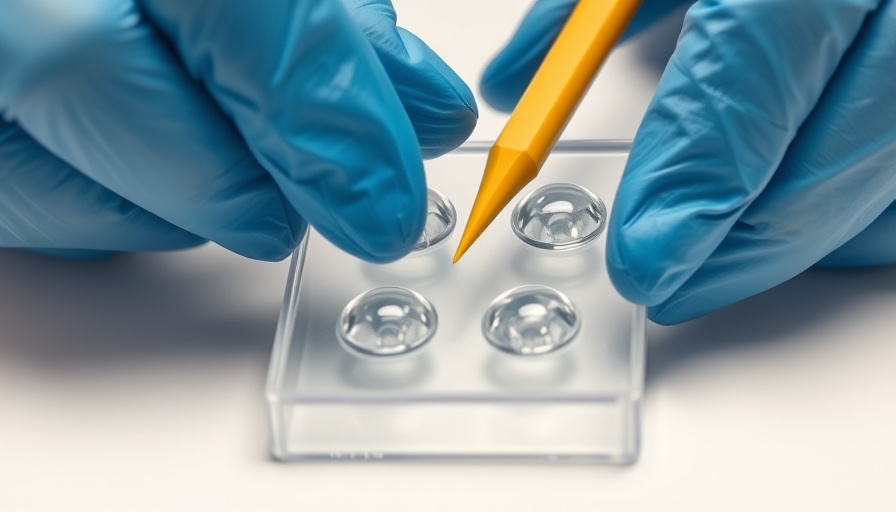

Revolutionizing Wound Care: The Role of Fish-Based Hydrogels in Artificial Skin
The importance of skin in protecting the human body cannot be overstated. Organizing a pivotal role in safeguarding against infections and environmental hazards, skin also contributes significantly to our overall health and appearance. With advancements in biotechnology, new solutions are emerging to address skin-related ailments. Among these innovations, the creation of artificial skin from fish-based hydrogels is a notable breakthrough poised to impact various medical fields significantly.
Understanding Fish-Based Hydrogels: What Makes Them Special?
Fish-based hydrogels, particularly derived from the gelatin extracted from cold-water fish like cod and pollock, provide an unmatched framework for developing artificial skin. This material can be easily manipulated and cross-linked to form a non-swelling hydrogel, perfectly suited for 3D printing processes. The biocompatibility of fish gelatin makes it an ideal candidate, reducing the risk of adverse reactions while mimicking the complex layering of human skin.
Pioneering Research: Empa's Innovative Approach to Artificial Skin
Researchers at the Swiss Federal Laboratories for Materials Science and Technology (Empa) are at the forefront of this exciting field. By constructing an artificial skin model enriched with cells, Empa's work enables simulated research on skin diseases. This initiative is part of SKINTEGRITY.CH, aiming to enlighten our understanding of conditions like skin cancer and autoimmune diseases. These insights are critical for healthcare practitioners as they seek better treatment protocols for affected individuals.
The Significance of Extracellular Matrix Simulation
Understanding the extracellular matrix (ECM) is vital as it provides structural support to tissues. In skin, different layers comprise unique ECM components. The fish-based hydrogels can closely mimic this ECM composition, facilitating the development of realistic models that accurately simulate skin functions. By leveraging this technology, medical professionals can better visualize and understand disease progression and treatment implications.
Bridging the Gap Between Technology and Patient Care
The integration of 3D printing technology in creating artificial skin models marks a significant leap forward. This manufacturing process allows for the precise placement of biological cells within the hydrogel. Medical practitioners can now envision new methodologies in treatment, research, and education, ensuring that care is firmly based on the latest advancements in science.
Future Trends: Anticipating Change in Medical Practices
As the field of bioengineering expands, we can expect fish-based hydrogels to rise in popularity for skin tissue engineering. Clinical practices will likely integrate artificial skin models for patient-specific treatments and wound care solutions. Moreover, with ongoing research, the potential for these materials extends beyond surgery into regenerative medicine and cosmetic applications.
Empowering Practitioners with Knowledge
As concierge health practitioners, it's crucial to stay informed about developments like fish-based hydrogels. Understanding their applications and benefits has the potential to revolutionize patient care strategies in your practice. To lead effectively, educators and practitioners alike must disseminate this knowledge to foster informed decision-making regarding skin treatments and technologies.
Take Action: Stay Ahead in Your Practice
As you navigate the complex web of modern healthcare practices, being informed about innovations like artificial skin models created from fish-based hydrogels is essential. Consider incorporating these insights into your practice and sharing them with colleagues; doing so fosters a collaborative approach toward enhancing patient outcomes.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 





Write A Comment