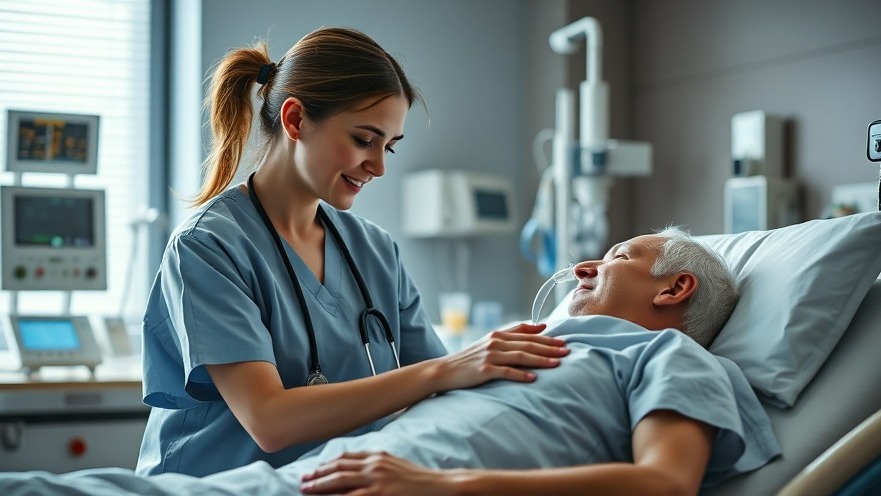

Understanding Ventilator-Induced Lung Injury
Recent research from Tulane University offers groundbreaking insights into the mechanics of ventilator-induced lung injury (VILI), a serious complication that has garnered significant attention, particularly during the COVID-19 pandemic. As healthcare providers grapple with an influx of patients requiring mechanical ventilation, the implications of this study underscore a need for reevaluation of current ventilation strategies.
The Cycle of Collapse and Reopening
Mechanical ventilation, while life-saving, has its drawbacks. The study identifies a specific mechanism—alveolar recruitment and derecruitment—where air sacs in the lungs repeatedly collapse and reopen. This action, which only accounts for a small percentage (2-5%) of energy used during ventilation, has significant ramifications. According to lead researcher Donald P. Gaver, biomedical engineering professor at Tulane, this cyclical process inflicts microscopic damage akin to "tiny explosions" at the delicate lung surface.
Impact on Patient Outcomes
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) affects approximately 10% of intensive care unit (ICU) patients, doubling their mortality risk. The implications of the study reveal that minimizing the repetitive collapse-and-reopening cycles could markedly improve recovery outcomes for critically ill patients. This aligns with findings in similar studies that reveal reduced energy dissipation correlates with better patient recovery rates.
Strategies for Optimized Ventilation
This study calls for a rethinking of intervention strategies in ventilated patients. Subsequent research should focus on developing real-time monitoring devices that quantify alveolar reopening events. By integrating this data, medical practitioners could tailor and optimize ventilation approaches to mitigate lung injury risk.
Future Directions in Mechanical Ventilation
The study not only highlights the complications of mechanical ventilation but also hints at broader implications for patient care worldwide. As we advance in our understanding of VILI, it opens avenues for developing ventilation protocols informed by real-time analytics. This shift in strategy could ultimately lead to the implementation of lung-protective ventilation methods that significantly lower injury rates among ventilated patients.
The Role of Technology in Patient Care
As healthcare technology continues to evolve, so too does the potential for transformative impacts in critical care settings. While the traditional approaches have served us well, it is evident that embracing technology capable of real-time monitoring and adaptive treatment could change the landscape of ICU care. Health practitioners should remain vigilant and informed about innovations that may enhance patient outcomes in the face of mechanical ventilation.
Final Thoughts and Call to Action
As healthcare professionals, staying ahead of emerging research is essential for improving patient care in challenging situations. The study from Tulane University is a timely reminder of how micro-level changes in ventilation strategies can lead to significant patient outcomes. Practitioners are encouraged to follow innovations in ventilation technologies and advocate for the integration of real-time monitoring systems in their hospitals, ensuring that the delicate balance of saving lives through mechanical ventilation does not come at the material cost of patients' lung health.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 





Write A Comment